HAREKAT PAVILION
Location Mazandaran, Iran
Date 2017
Employer University of Mazandaran
Sponsor University of Mazandaran
HAREKAT PAVILION
Mazandaran, Iran | 2017
Designers: MEHRDAD AZIZKHANI, ELHAM SHAHABI, ALI NAKHAEI, NEDA YOUSEFI
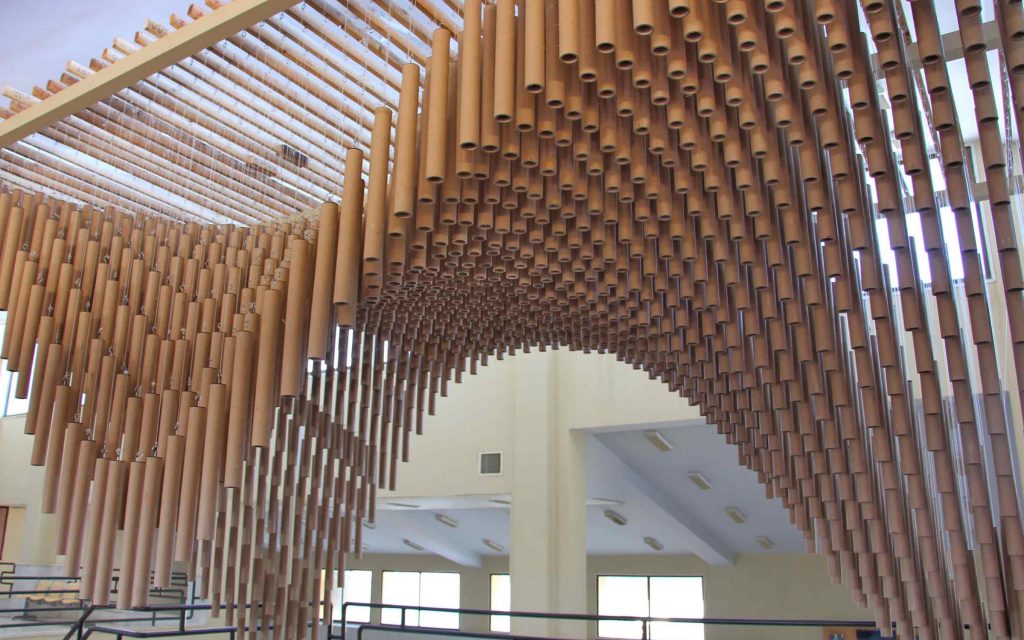
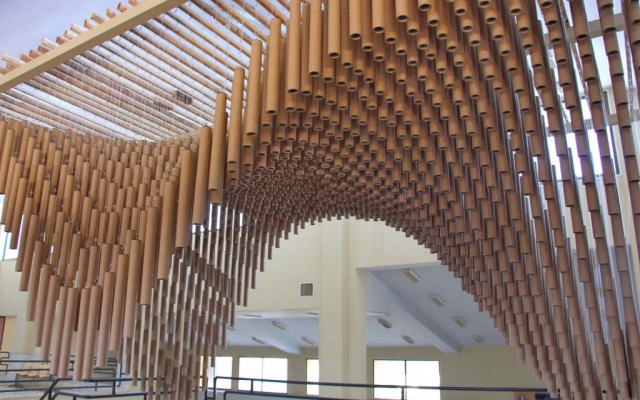
The pavilion was set up to showcase the research achievements of the universities present at the 10th Harakat Festival during the Computational Design and Digital Fabrication Workshop. The pavilion was designed to be able to reassemble again. Using this feature, first built at Mazandaran University and then rebuilt in Kermanshah. All the presented pavilions in the festival were judged, and the mentioned pavilion was selected as the best project.
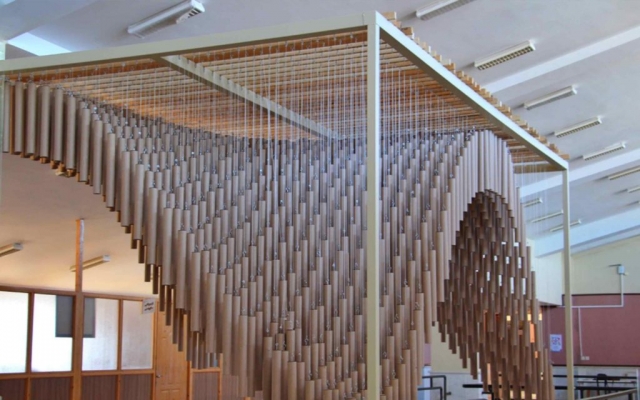
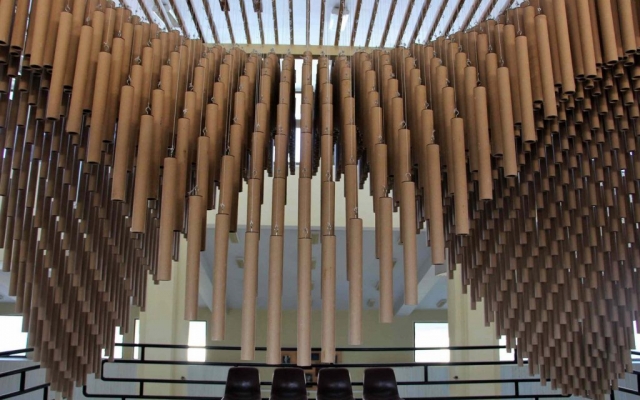
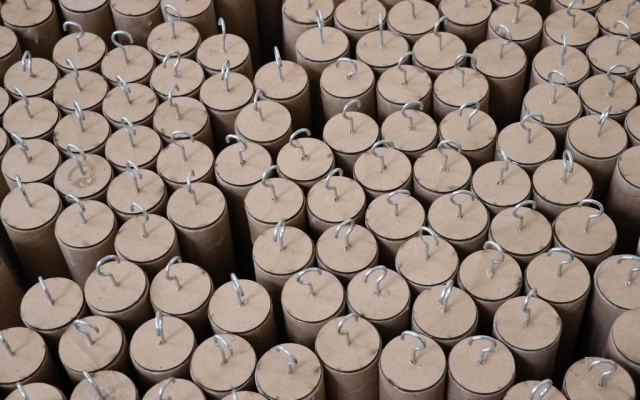
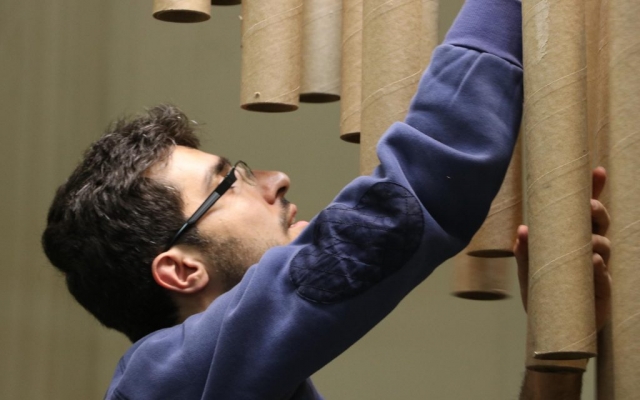
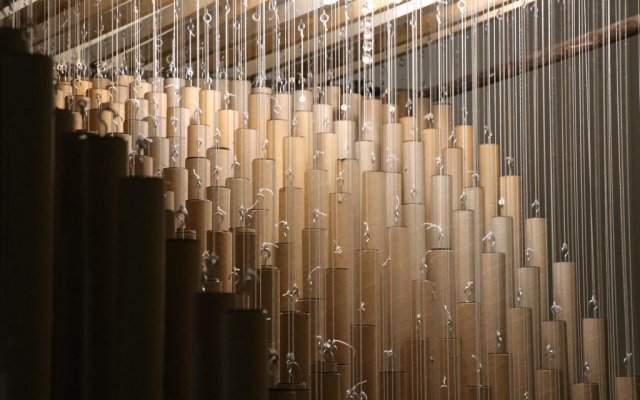
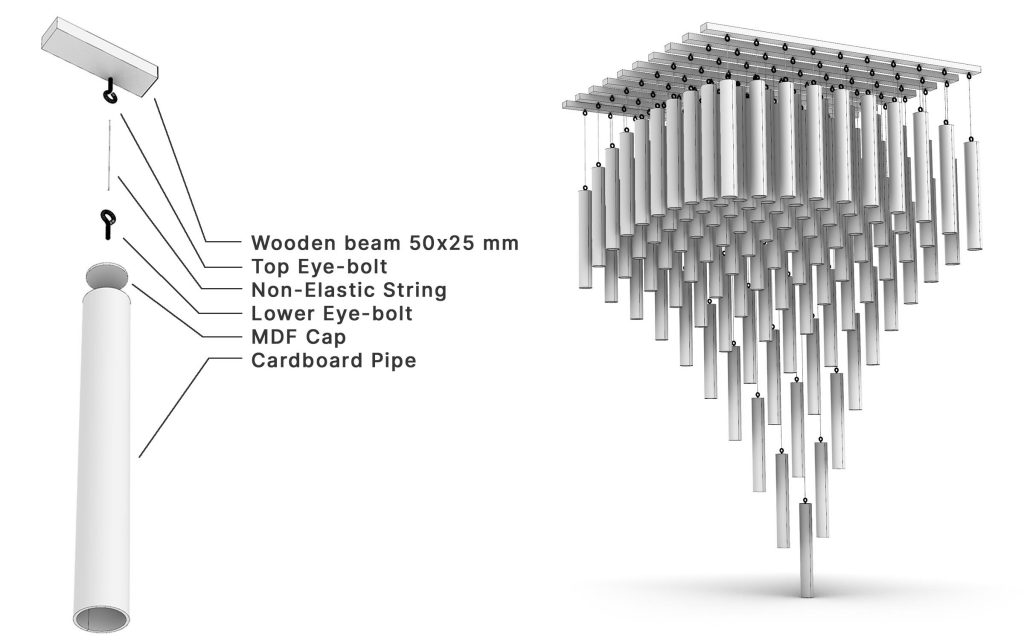
Construction with recycled materials has been an influencing factor in project design. Therefore, cardboard tubes with a fixed length of 500 mm and a diameter of 40 mm, and a thickness of 5 mm, previously used as paper and fabric roll holders, were collected over a specified period and were used as the principal material. The beams were held on a metal frame, and the pipes were attached to the beams using strings of specific sizes.
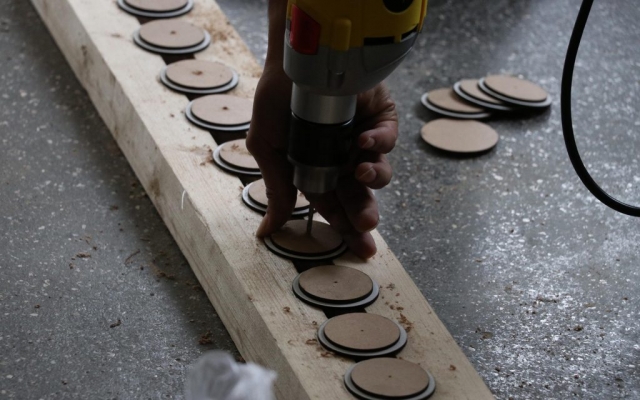
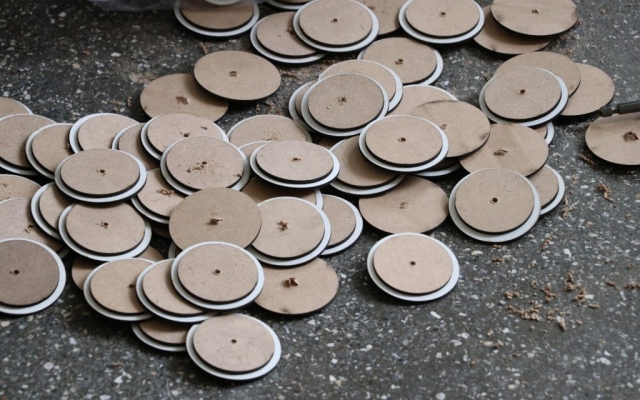
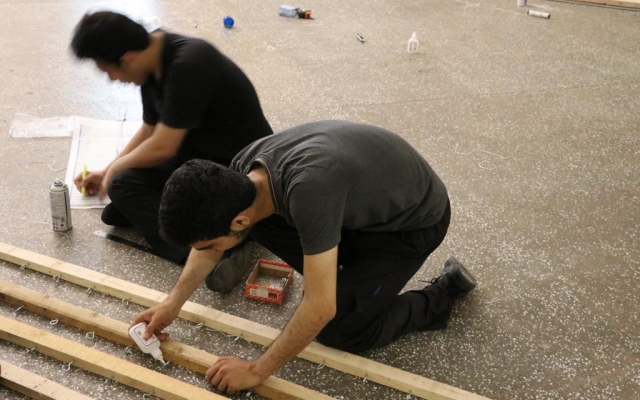
The eye screws were used in the center of 4 mm thick MDF caps, To connect the tubes and the cut strings. Finally, the strings length table was extracted from the software, which was necessary to begin the construction in several groups. The pipes were installed in groups of 28 on 45 wooden beams. The support structure of the pavilion was made of square iron profiles.
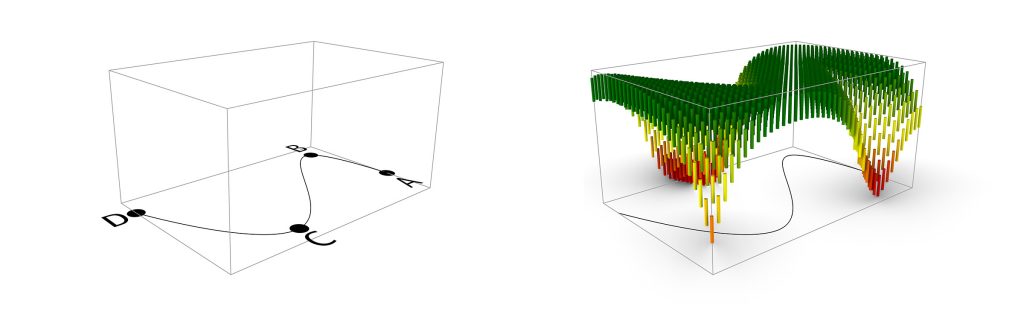
A genetic algorithm (Galapagos) was used in the pavilion’s design process to optimize the points’ height. This way, A and D points on the outer edge and B and C points inside the pavilion plan were produced. The minimum distance between the points of the first group should not be less than 1.5 meters. On the other hand, the second group of points could move freely inside the plan by maintaining a distance of 50 cm from the edge. Then all the points became an interpolated curve. The following rules were asked from the algorithm as a fitness factor:
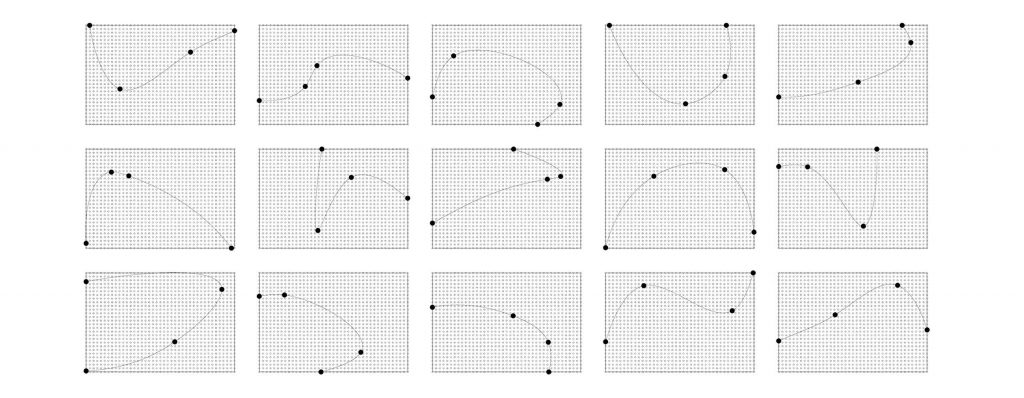
• The final curve should not intersect
• The distance between points A and D should not be less than 1.5 meters
• The number of points that were occupied was minimized
• The length of the curve was maximized